
Solar panels are a great investment for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint and save money on their energy bills. However, like any technology, solar panels can experience issues over time. It’s important to know how to tell if a solar panel is bad so that you can address any problems as soon as possible.
There are several signs that can indicate a faulty solar panel. One of the most obvious signs is a decrease in energy production. If you notice that your solar panel is not producing as much energy as it used to, it could be a sign that something is wrong.
Another sign to look out for is physical damage to the panel, such as cracks or scratches. In some cases, a bad solar panel may also cause your inverter to display an error message.
Table of Contents
How to Know if a Solar Panel is Bad
To determine if a solar panel is bad, look for signs such as decreased energy production, physical damage or discoloration, hot spots, potential-induced degradation (PID), and monitoring system alerts.
If the panel generates significantly less electricity, has cracks or dark spots, exhibits excessive heat in specific areas, shows signs of PID, or triggers monitoring system alerts, it may be faulty.
In such cases, it is advisable to seek the expertise of a professional solar technician for a thorough evaluation and appropriate remedies. Here are some other ways to tell, along with some more detailed information.
Decreased Energy Production
One of the most evident signs of a faulty solar panel is a noticeable decrease in energy production. If your solar system is generating significantly less electricity than it used to, it could indicate a problem with one or more panels.
To identify if a particular panel is causing the issue, you can compare the energy output of each panel using a monitoring system or by analyzing your electricity bills over time. If there is a significant drop in energy production from a specific panel, it may be defective.
Physical Damage or Discoloration
Inspecting your solar panels regularly for physical damage or discoloration is crucial. Hailstorms, fallen debris, or extreme weather conditions can cause cracks, chips, or scratches on the surface of the panels.
Additionally, discoloration or dark spots on the panel’s surface may indicate damage or potential issues with the solar cells. If you notice any visible signs of physical damage or discoloration, it is advisable to contact a professional to assess the situation.
Hot Spots
Hot spots occur when a specific area of a solar panel becomes significantly hotter than the surrounding areas. These hot spots are often caused by manufacturing defects or cell damage, and they can adversely affect the performance and longevity of the panel.
To identify hot spots, you can use thermal imaging cameras or consult a solar professional who has the necessary equipment to conduct a comprehensive inspection.
PID (Potential-Induced Degradation)
Potential-Induced Degradation, or PID, is a phenomenon that affects the performance of solar panels. It occurs when voltage potential between the solar cells and the panel frame creates an electrical leakage, leading to power loss over time. PID is more common in older panels or those with poor grounding or insulation.
To diagnose PID, you can hire a solar technician to perform a test known as the “EL imaging” test, which can identify the extent of PID and recommend suitable remedial measures.
Monitoring System Alerts
If your solar panel system is equipped with a monitoring system, it can be a valuable tool for detecting any anomalies or issues with individual panels.
These systems provide real-time data on energy production and can alert you to any significant variations or irregularities. Monitoring systems may display error codes, low voltage readings, or panel-specific alerts, indicating potential defects that require further investigation.
Solar Monitoring Systems for Residential Solar
By providing real-time data and insights, solar monitoring systems allow homeowners to track their solar panels’ performance, energy production, and consumption patterns. This information lets users make informed decisions, identify potential issues, and maximize their solar energy savings.
One of the key advantages of solar monitoring systems is their ability to offer comprehensive and detailed analytics.
Homeowners can access a user-friendly dashboard that displays key performance indicators such as solar panel output, sunlight exposure, and historical energy production. With this data readily available, residents can accurately assess the effectiveness of their solar investment.
Monitoring systems often come equipped with alert mechanisms, notifying homeowners of any abnormalities or drop in performance. This proactive approach ensures prompt troubleshooting and maintenance, minimizing downtime and maximizing overall energy generation.
The integration of smart technology into residential solar monitoring systems further enhances their usability and functionality.
Many modern monitoring platforms support mobile applications, enabling homeowners to access vital solar data on the go.
Whether they are at home, work, or traveling, users can monitor their solar system’s performance from their smartphones or tablets.
Additionally, these systems can be connected to smart home ecosystems, allowing seamless integration with other energy-saving devices. Such compatibility enables homeowners to optimize their energy consumption, adjusting usage patterns to coincide with peak solar production, leading to even greater energy and cost savings.
Solar monitoring systems align perfectly with the worlds growing eco-friendly ethos by promoting renewable energy usage and reducing carbon footprints.
By actively monitoring their solar panel performance, users can ensure their systems are operating at their peak efficiency, avoiding energy wastage and unnecessary expenses. This heightened efficiency translates to a reduced reliance on traditional power sources and a more sustainable way of living.
As an added benefit, homeowners with solar monitoring systems often have access to incentives and rebates, further encouraging the adoption of residential solar solutions.
Measuring Solar Panel Performance
Why Measure Solar Panel Performance?
Measuring the performance of a solar panel is important to ensure that it is functioning optimally. A solar panel’s performance can be affected by various factors, such as shading, dirt, and temperature. Measuring the performance of a solar panel can help identify any issues that may be affecting its output and allow for corrective action to be taken.
What to Measure
When measuring the performance of a solar panel, there are a few key metrics to keep in mind:
- Current (Amps): The amount of electrical current produced by the solar panel.
- Voltage (Volts): The electrical potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of the solar panel.
- Power Output (Watts): The amount of electrical power produced by the solar panel.
- Efficiency: The percentage of sunlight that is converted into electrical power by the solar panel.
How to Measure
Measuring the performance of a solar panel can be done using a solar meter or a multimeter. Here are the steps to measure the performance of a solar panel using a multimeter:
- Set the multimeter to measure DC voltage.
- Connect the positive lead of the multimeter to the positive terminal of the solar panel, and the negative lead to the negative terminal of the solar panel.
- Measure the open-circuit voltage (OCV) of the solar panel.
- Measure the short-circuit current (SCC) of the solar panel.
- Calculate the power output of the solar panel using the following formula: Power Output = OCV x SCC.
It is important to note that measuring the performance of a solar panel should be done under standard test conditions (STC), which include a temperature of 25°C, an irradiance of 1000 W/m², and an air mass of 1.5.
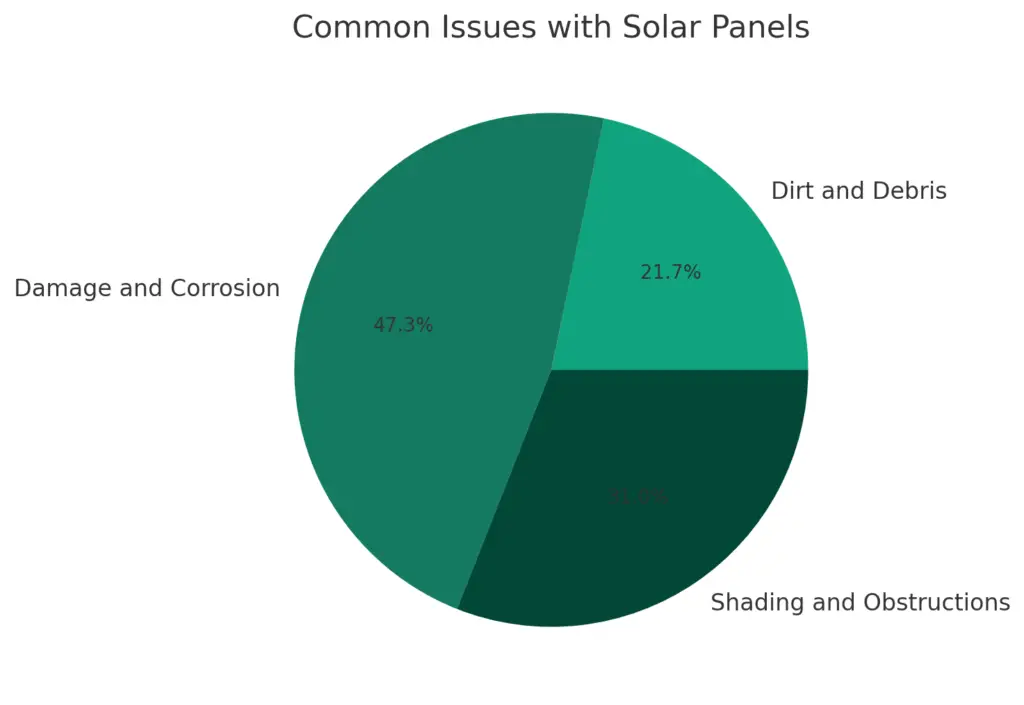
Common Issues with Solar Panels
Solar panels are a reliable and efficient way to generate electricity, but they are not immune to problems. Here are some common issues with solar panels that you should be aware of:
Dirt and Debris
Dirt and debris can accumulate on solar panels over time, reducing their efficiency. It is important to clean your solar panels regularly to prevent this from happening. You can use a soft-bristled brush or a hose to remove dirt and debris from your solar panels.
Damage and Corrosion
Solar panels can be damaged by weather, birds, rodents, and other factors. Damage can lead to underperforming solar panel output, and in some cases, a short circuit current. It is essential to inspect your solar panels regularly to detect any damage or corrosion. If you find any damage, you should replace the affected components immediately.
Shading and Obstructions
Shading and obstructions can significantly reduce the efficiency of your solar panels. Trees, buildings, and other objects can cast shadows on your solar panels, preventing them from receiving direct sunlight. It is important to install your solar panels in a location that receives direct sunlight for most of the day. If you notice shading or obstructions, you should consider relocating your solar panels.
In addition to these issues, other problems can affect the performance of your solar panels, such as faulty wiring, microcracks, hot spots, snail trails, discoloration, and microscopic cracks. It is important to have your solar panel system regularly inspected by a professional to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
Remember that solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, which must be converted to alternating current (AC) using an inverter before it can be used. The inverter is an essential component of your solar panel system, and it should be inspected regularly to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
Testing Solar Panels
Solar panels are an essential component of solar energy systems, and it is vital to ensure they are functioning correctly.
When to Test
It is recommended to test solar panels at least once a year to ensure they are working correctly. However, if you notice a decrease in energy production or other signs of malfunction, it is essential to test them immediately. Some signs of a faulty solar panel include:
- Reduced energy output
- Physical damage to the panel
- Discoloration or discoloration of the panel
- Loose wiring or connections
How to Test
To test a solar panel, you will need a multimeter, which measures the voltage and current output of the panel. Follow these steps to test your solar panel:
- Turn off the solar panel system to ensure your safety.
- Set the multimeter to measure DC voltage.
- Connect the positive and negative leads of the multimeter to the corresponding terminals of the solar panel.
- Place the solar panel in direct sunlight and take a reading of the voltage output.
- Calculate the wattage by multiplying the voltage by the amperage output of the panel.
If the voltage output is lower than the panel’s rated voltage, there may be a problem with the panel or the wiring. If the voltage output is higher than the panel’s rated voltage, it may indicate a problem with the charge controller or other components of the solar energy system.
Maintenance and Warranty
Solar panels are generally low-maintenance, but it is still important to take care of them to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Additionally, understanding the warranty that comes with your solar panels can help you protect your investment and avoid costly repairs.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Most solar panels require little or no maintenance, but it is still important to keep them clean to ensure maximum energy production. Dirt, dust, and other debris can accumulate on the surface of the panels, reducing their efficiency. Regular cleaning can help prevent this buildup and ensure that your panels are producing as much energy as possible.
If you need to clean your solar panels, it is generally best to hire a professional cleaner. They will have the necessary equipment and expertise to clean the panels safely and effectively. Additionally, many solar panel manufacturers offer cleaning and maintenance services as part of their warranty.
Warranties and Repairs
Understanding the warranty that comes with your solar panels is important to protect your investment and avoid costly repairs. There are two main types of warranties that cover solar panels: product warranties and performance warranties.
A product warranty protects you from defects in the solar panel materials or manufacturing errors. These warranties typically last for 10-25 years, depending on the manufacturer. Performance warranties, on the other hand, guarantee that your solar panels will produce a certain amount of energy over a specified period of time. These warranties typically last for 25 years.
If you experience any issues with your solar panels, it is important to contact the manufacturer or installer right away. They will be able to diagnose the problem and determine if it is covered under warranty. If it is not covered under warranty, they can provide you with a quote for repairs.
Understanding Solar Panels
What are Solar Panels?
Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells that are connected together to form a module. These modules are then wired together to form a solar system that can produce enough electricity to power homes, businesses, and even entire cities.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
When sunlight hits a solar panel, it is absorbed by the PV cells. The cells then convert the sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. An inverter then converts the DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used to power homes and businesses.
Types of Solar Panels
There are three main types of solar panels: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film.
- Monocrystalline solar panels are made from a single crystal of silicon and are the most efficient type of solar panel. They are also the most expensive.
- Polycrystalline solar panels are made from multiple crystals of silicon and are less efficient than monocrystalline panels. However, they are also less expensive.
- Thin-film solar panels are made from layers of photovoltaic material that are applied to a substrate. They are the least efficient type of solar panel but are also the least expensive.
Solar Panels and Renewable Energy
The Benefits of Solar Energy
Solar energy is a renewable energy source that is generated through the conversion of sunlight into electricity. It is a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels, which are non-renewable and contribute to environmental pollution. By installing solar panels, homes and businesses can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and lower their carbon footprint.
In addition to being environmentally friendly, solar energy can also save you money on your electricity bills. Once you have installed solar panels, you can generate your own electricity and reduce your reliance on the grid.
This means that you can save money on your electricity bills and even earn money by selling excess electricity back to the grid.
Solar Incentives and Tax Credits
To encourage the adoption of solar energy, many states and the federal government offer incentives and tax credits for businesses and homeowners who invest in solar panels.
The federal solar investment tax credit (ITC) allows homeowners and businesses to deduct a percentage of the cost of installing solar panels from their federal taxes. In California, homeowners can also take advantage of the California Solar Initiative, which provides rebates for the installation of solar panels.
Solar Energy Regulations
As solar energy becomes more popular, there are regulations in place to ensure that solar panels are installed safely and efficiently. For example, solar panels must be installed by licensed professionals and must meet certain safety standards. Additionally, there are regulations in place to ensure that excess electricity is safely and efficiently fed back into the grid.
